Abstract:
This Technical Description, for me, was the Ideal project for this class, this project covered the main learning outcome of this course, Technical communication, and what makes it different from general communication, It taught me the balance between being too descriptive and being too vague, this technical description of Bitcoin, the functionality, and the usage, is something not everyone would understand easily, but I learned how to use simple language that anyone who knows anything about digital currency or digital banking, could easily understand the idea behind bitcoin. The learning outcome of this project is something that I would use in real-time.
Introduction
In this era where everything is digitalized, we can consider Bitcoin to be a digitalized Currency, now one might ask that the general banking facility has already been almost digitalized and everyone has been using it for a while now, we can send or receive our currency or make payments using the money that we have in our accounts, without having to go physically and withdraw. So, what makes Bitcoin special? Or why should we use it?
In 2007 Satoshi Nakamoto Created the bitcoin as a digital ‘Decentralized’ Currency; Notice the term ‘Decentralized’, this means that the bitcoin is purely peer-to-peer version of digital currency, which makes bitcoin one of the safest ways to make transactions considering the current process that financial institutions work on; because if you want to make a transaction it doesn’t have to go through any “trusted” financial institution to validate your transaction. When one says bitcoin is decentralized, it means that it is not stored anywhere physically like the cash in our bank accounts; it doesn’t have a central and rigid storage. This makes it very secure because if it was stored somewhere, then it could easily be accessible to a hacker, and they can take away all your assets if they just get access to that central unit (ex: your bank account). When the digital era began, people didn’t care about the security of their bank accounts, but progressively we can see people are concerned about their privacy and security. You can see in the data below in fig (1) that over time people have started using p2p (peer-to-peer) transactions and the estimated evaluation of p2p transaction up to 2030 in the US.

Fig (1)
Creation of Bitcoin
In this section, you are going to find the answer to the question, why was bitcoin created? Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency to ever exist, it was created somewhere around 2007-2009 when the distrust of governments and banks was at peak. It was introduced as an alternative to the fiat currency, which was controlled by the government and central banks of the country. Satoshi Nakamoto, who has remained an unknown figure to the world; but the reason he created bitcoin was pretty clear, the basic reason for Nakamoto to create bitcoin was to gain the financial control back from the government and central banks, who control our money. Isn’t it weird how we just give our most valuable assets to the government and banks, and just trust them with it. Nakamoto wanted to make people feel safe and secure when it comes to their currency, Crypto currency is the only way where you can store your financial assets, and only you know the data that’s in it, and bitcoin is the instance to do that.
Functionality
The two fundamental aspects of bitcoin’s functionality are:
- Blockchain
- Peer-to-peer
- Decentralization
BLOCKCHAIN: the simplest synonym of blockchain could be “A digital Ledger”, Blockchain can be used in many ways, but it’s mainly used in cryptocurrency, in this case the usage of blockchain is as a ledger for our bitcoin transactions, every time a transaction has been made a block is added to the ledger, but the addition of the block is what makes it special, the mining process in bitcoin is unique. The mining of blocks refers to the process in which a block is added to the blockchain when a transaction is made, this addition of block is very secure but also at the same time very tedious. When a transaction is made, the miners of the bitcoin work in an algorithm called “proof of work”, in which the miners validate the transaction and add a block to the blockchain. The miners go through some crypto graphic key which will be with the recipient and through that they will check the authorization of the recipient, add a block to the blockchain, and that blockchain is distributed among the network, now here comes the part where things get quite secured, suppose one of the peers in the network wanted to change the ledger and modify a transaction, when that happens the miners who are responsible for the addition of blocks, will validate this by checking the blockchain throughout the network, if the data in the blockchain does not match to the data that is with other peers in the network then they can easily find out who tried to modify the blockchain and even if hackers can get access to the blockchain, they can’t modify it in any way, the miners can easily check the authority of the user who has accessed the blockchain through the proof of work algorithm, by the way the functionality of this algorithm is quite abstract.
PEER-TO-PEER: the blockchain technology on which bitcoin is based on, eliminates the intermediaries (ex: Banks), suppose you have to transfer funds to someone, one of the ways you can do that is by physically going out, withdrawing and delivering the cash to the recipient, but in this modern era most people won’t resort to that way, they would want a more efficient and fast way, and probably a secure way. in a NON p2p transaction which ensures time efficiency and expeditious delivery, but not security. As we know in this digital age where technology is growing so much, but simultaneously the ways to break those technologies is also increasing; to save ourselves from a breach to our valuable assets that are stored in a digital storage or in this case make modifications in our digital ledger, we can use p2p technology, which is based on blockchain – the most secure digital ledger the world has known, in which it is almost impossible to modify the ledger, and it also makes the transaction without intervention of a financial institution.
Decentralization: The decentralization in blockchain, is what makes it special; the decentralization technology basically means the transfer of control of your financial assets from financial institutions like Government, Central bank etc. to directly in your hands. This technology on which blockchain works on, strives to reduce the that participants must put in one another in case of their valuable assets to direct cryptographic proof of work system. When these assets are centralized, they can be as secure as they want but their rigidness makes them vulnerable, because if the hackers get access to their address, then they can easily steal what’s inside of it but if it’s decentralized and it keeps circulating among the network then no one can access it easily, because the address of the storage keeps changing and it’s stored in a cryptographic way, with billions of permutations and combinations which no hacker can decode. You can see the fig (2) to understand what it means by decentralized and spread among the network vs what a centralized storage means.
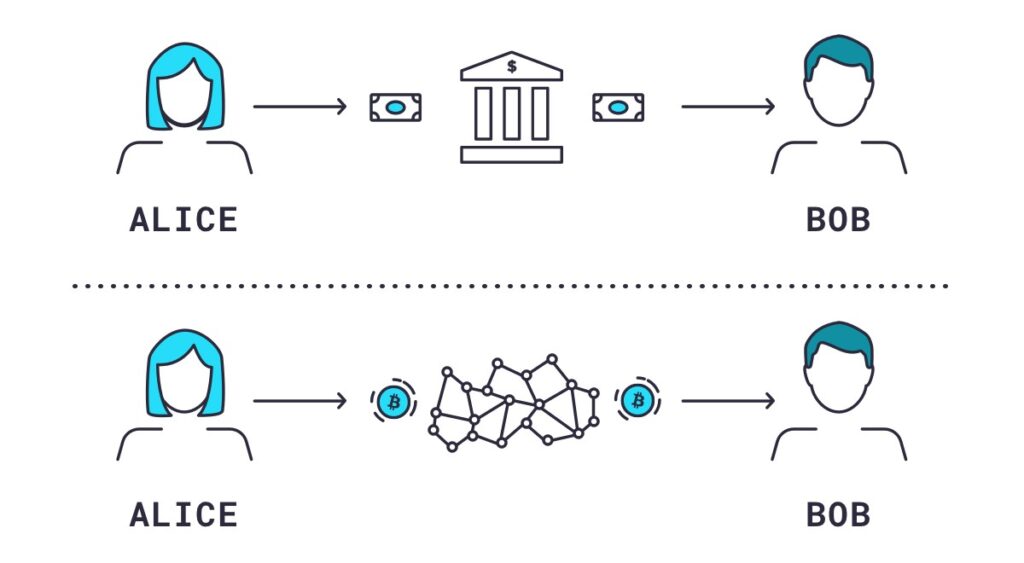
Fig (2)
- In the above picture the centralized system shows that the transaction is occurring through a financial institution, which is based completely on trust, practically speaking, the possibilities of a breach and corruption are very high in the centralized system.
for example:
- your money is stored somewhere safe in the locker of the bank and what if someone breaks in to the bank and robs all the money
- what if the bank gets corrupted and it shows from your side that the transaction has been made and they provide you with a modified ledger with a fake transaction in it.
- In the decentralized storage your all your financial assets are stored in a network and it keeps circulating throughout the network where no one can access it easily, and instead of trust you can get a proof of the work or the transaction and be assured that it was successful.
Advantages & Disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Bitcoin is quite secure and no hackers can easily access it.
- The ledger of the bitcoin is irreversible.
- No financial institution can intervene with your financial assets.
- Transaction costs in bitcoin are very low to almost nothing.
- Used for trading and investment.
Disadvantages:
- Bitcoin technology is still in development
- Not everyone in the world can get access to bitcoin and use it as a real currency.
- Bitcoin being a completely digital currency, so there is chance that bitcoin wallets can easily get lost if the computer hard drive fails.
- Value of bitcoin keeps fluctuating; this means that if you buy bitcoin with a certain value and when you sell It there is a chance that the return value is not the same anymore.
Conclusion:
In this constantly growing, digital era, there is a chance that cryptocurrency could be used full time now or soon, and bitcoin is the standard instance of cryptocurrency. Bitcoin is very secure and useful but unstable at the same time; Bitcoin is just ahead of its time, and people don’t realize that they need it yet.
This technical description of bitcoin gives you a lucid image of what a bitcoin is and how it works, and the practical nature of it. Bitcoin’s inventor Nakamoto invented this to make people safe and give them control over their financial assets, but Bitcoin in itself is very complex in structure, and works on high level technologies like blockchain and decentralized network. Bitcoin’s peer to peer process of making transactions and storing the ledger of those transactions in a blockchain and maintaining the blockchain in a decentralized network requires very strong computing power, which an average computer can’t handle yet, that’s what makes it ahead of its time.
Bitcoin is the future
References:
Images:
https://www.forbes.com/advisor/in/investing/what-is-bitcoin-and-how-does-it-work
https://www.precedenceresearch.com/p2p-payment-market
Blockchain
https://www.synopsys.com/glossary/what-is-blockchain.html
Decentralization
https://aws.amazon.com/blockchain/decentralization-in-blockchain/
Advantages and disadvantages
https://cs.stanford.edu/people/eroberts/cs181/projects/2010-11/DigitalCurrencies/disadvantages/


